- ekkeuustalu
- 0 Comments
- 247 Views
Welcome to this blog post about URL forwarding, commonly known as “redirects”. The internet is a dynamic space, with webpages constantly evolving, moving, or disappearing. For various reasons, website owners may need to direct visitors from one webpage to another. Redirects make this possible. Let’s delve into the world of URL forwarding and see why it’s such an essential tool for webmasters.
What Are Redirects?
Redirects or URL forwarding is the process where a single URL is pointed to another URL. Essentially, when a user attempts to visit a specific URL (the source URL), they are automatically sent to a different URL (the target or destination URL). This action is usually seamless, and the user may not even be aware it has occurred.
Why Are Redirects Important?
Redirects are crucial for numerous reasons:
- Website Renovation: Websites are often restructured, and as part of this, URLs might change. Redirects help ensure users and search engines find the correct pages after the changes.
- SEO: By properly implementing redirects, you maintain your site’s SEO rankings. When a page with a high ranking is deleted or moved without a redirect, its search engine ranking is lost.
- User Experience: Redirects prevent users from encountering broken links and ‘404 not found‘ errors, thereby enhancing their browsing experience. Additionally, they allow you to shorten or simplify your links which you can share with your users.
- Security: HTTPS redirects are crucial for moving users from HTTP to the more secure HTTPS version of a site.
When to Use Redirects
Redirects should be used in the following instances:
- Site or Page Moves: If you’re moving your site to a new domain or relocating specific pages, redirects will help maintain your SEO efforts and guide visitors to the correct location.
-
Making Links More Memorable: For example, your users are more likely to remember a link that looks like
example.com/great-contentas opposed toblog.example.com/2022/05/our-great-overview-of-the-current-trends. - Deletion of Pages: If you remove a webpage that users may have bookmarked or linked elsewhere, you can set up a redirect to send visitors to a relevant, existing page.
- HTTP to HTTPS: As part of establishing a secure browsing environment, users trying to access the HTTP version of your website should be redirected to HTTPS.
Types of Redirects
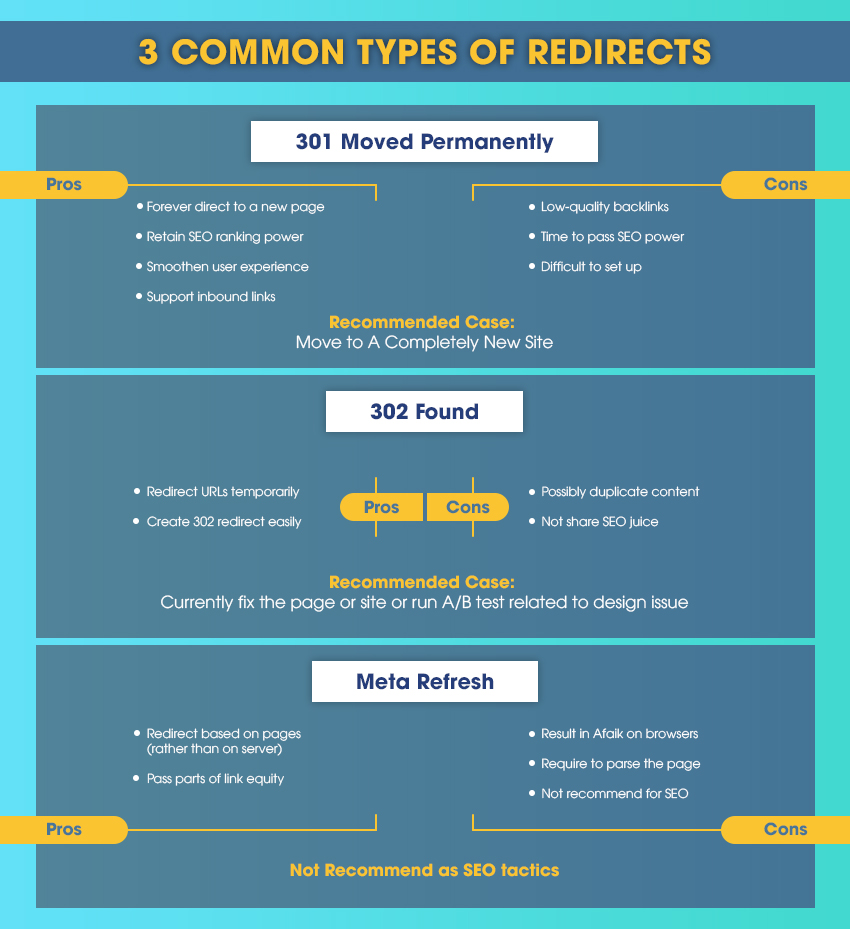
There are several types of redirects, but the most common are 301, 302, and meta refresh redirects:
- 301 (Permanent) Redirect: This indicates that the page has moved permanently. It is most commonly used when moving a site to a new domain or restructuring a website.
- 302 (Temporary) Redirect: This is used when a page is moved temporarily, for instance, during a website redesign or maintenance.
- Meta Refresh: This is a form of redirect implemented on the page level rather than the server level. It is often used for timed redirects (like “You will be redirected in 5 seconds”).
10 Redirect Best Practices
Here are some best practices for implementing redirects:
- Use 301 Redirects for Permanent Moves: This tells search engines that the old page is no longer relevant and transfers the link equity to the new page.
- Avoid Redirect Chains: These are multiple redirected jumps from the source to the final URL. They can cause slower loading times as each redirect requires additional processing and loss of link equity. The loss of link equity is considered to be up to 85% per redirect. This means that after 5 redirects, the carried-over value is only around 44%.
- Update Your Internal Links: When you move a page, don’t just set up a redirect; also update the internal links pointing to that page.
- Be Relevant: Make sure your redirects send users to a page with similar content. Misleading redirects can frustrate users and harm your SEO. Google is becoming more and more advanced when it comes to evaluating the usefulness (they call it people-first) of your content. If you are maliciously redirecting users and not showing them what they expected to see, you could be penalized.
- Carefully Implement Wildcard Redirects: Wildcards can redirect large sets of URLs, but they should be used carefully to avoid unintentional redirects. With great power comes great responsibility – wildcard catch-all redirects can accidentally also overrule some explicit redirects that you wanted to redirect to some other place.
- Prefer HTTPS over HTTP: Redirect users to the secure HTTPS version of your site to protect their information. This is now the standard way for most hosting providers and platforms anyway, but you might have to make some adjustments for some older pages.
- Avoid Meta Refresh: These can confuse users and aren’t always recognized by search engines.
- Test Your Redirects: Always test your redirects after implementation to make sure they work as intended. You can find various tools online, but the one we often come back to is this redirect checker.
- Monitor Performance Post-Redirect: Keep an eye on your analytics to see if there are changes in traffic or search engine ranking after the redirect.
- Regularly Audit Your Redirects: Ensure all redirects are still needed and functioning correctly.
Redirect FAQs
Q: Do redirects affect SEO?
A: Yes, poorly implemented redirects can harm your SEO, but correctly implemented ones can maintain or even boost your ranking. For example, 301 redirects will carry over the SEO value whereas 302 will not.
Q: Can redirects be undone?
A: Yes, you can remove a redirect anytime. However, this should be done carefully as it could affect your site’s SEO and user experience. Just make sure you only remove redirects that haven’t had any relevant traffic and that you don’t link internally anymore.
Q: How many redirects are too many?
A: It’s best to avoid chains of more than three redirects. Long redirect chains can slow site loading times and confuse search engines (confusing them means that your content will not be valued as high as it would be without the redirects).
Q: How can I set up redirects?
A: It really depends on the type of redirect you want to implement, your domain registrar, and your technical knowledge. We have put together a guide on how to redirect one domain to another using a variety of tools.
Conclusion
Redirects are a powerful tool when maintaining, moving, or restructuring a website. They allow for a smoother user experience, improved security, and the preservation of hard-earned SEO rankings. However, they should be used judiciously and monitored carefully to ensure they are achieving their intended purpose.


